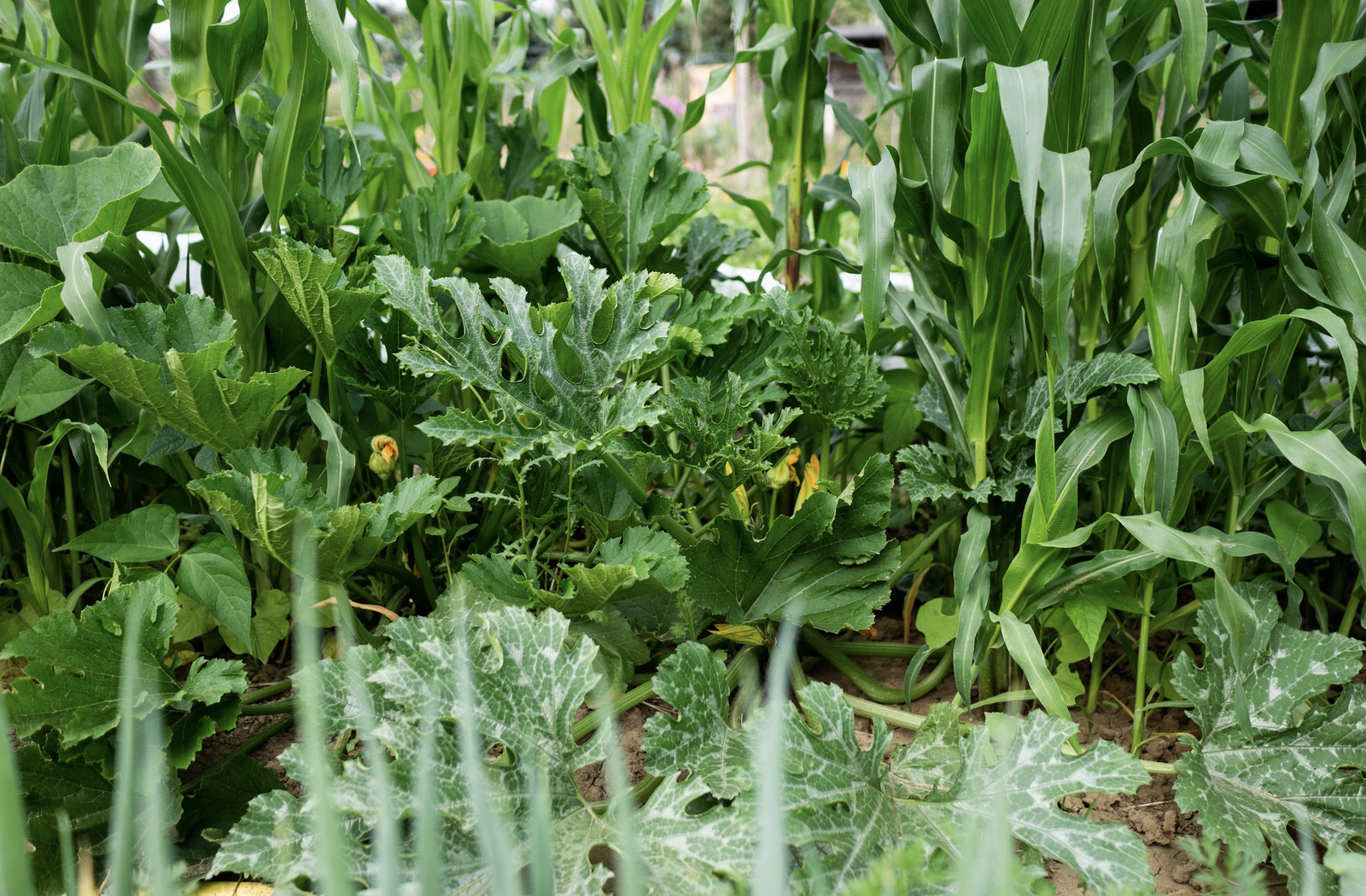
Companion Planting: What Vegetables Go Best Together? (With PDF)
Mixed cultivation is about combining plants that have a positive effect on each other and protect against pests. We have created a list of companion plants here, which you can easily download for free.
This Article Contains:
- A Guide to Companion Planting
- Companion Cropping: Examples for Your Vegetable Bed
- Examples for Your Planting Plan With Tomatoes
- Milpa Planting Plan: Ideas & Examples
- Ideas for Your Companion Cropping With Cucumbers
- Table with companion plants for vegetables
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Mixed Cropping
Quick Overview
Companion Planting: Table as an Overview
Here you can find the table as a PDF download.
Advantages of Mixed Cultivation
- Promotes and maintains soil fertility
- space in the vegetable patch is optimally utilized
- Increases diversity in the garden
- attracts beneficial insects, keeps so-called pests away
Examples of Mixed Crops
- Tomato with basil, parsley and/or marigold
- Corn, beans and pumpkin (alternatively peas instead of beans); you can also replace the pumpkin with other pumpkin plants or potatoes
- Cucumbers with dill, borage and onion plants
- Carrots and onions: leeks are more suitable than onions
- Strawberries and onions; borage and marigolds also go well with strawberries
A Guide to Companion Planting
Mixed Cultivation Promotes Soil Fertility
Like us humans, plants have different characteristics - need more or less nutrients, have deep or shallow roots. Some plants are well suited to each other due to their site requirements and growth habit. Some species get on particularly well together because they complement each other in terms of their nutritional requirements and are not affected by similar diseases and pests. At the same time, mixed cultivation also ensures that the soil is not depleted by combining plants with high nutrient requirements with plants with low nutrient requirements.
Optimum Use of Space in the Bed
In addition to the nutrient requirements, a successful mixed crop also takes into account the different growth forms of the above-ground plant parts as well as the underground roots of the vegetable varieties. If, for example, tall-growing vegetables such as corn and runner beans are planted underneath ground-covering pumpkins, you can plant a little more densely and make better use of the available space.
Diversity in the Bed Against Pests
Another major advantage of mixed cultivation is that you have a wide variety of plants in your bed. Problems of monoculture, such as the large-scale spread of crop-specific diseases and pests, can be prevented with mixed cultivation. This is because different crops attract a wide variety of beneficial insects and pests that can regulate each other.
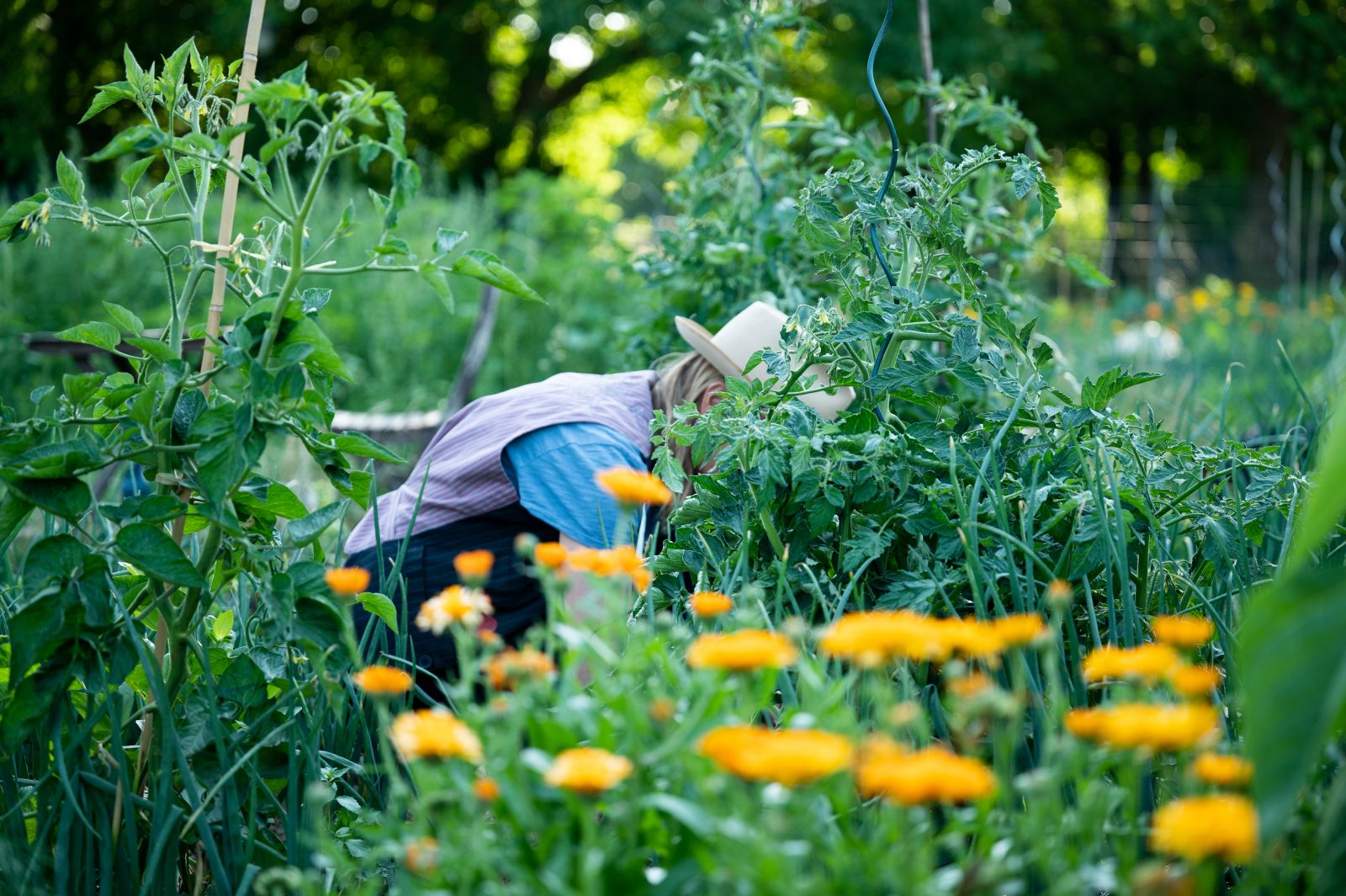

Want to Plan a Bed With Companion Plants?
With our bed planner, you can easily plan a colourful mixed crop. Good and bad companion plants are displayed directly and you get tips on succession planting and crop rotation!
Plan Your Bed NowCompanion Cropping: Examples for Your Vegetable Bed
Tomatoes in a Mixed Crop: The Classic - Basil and Tomato
This mixed culture is a classic and works well together. Basil keeps whitefly away from the bed. It also has a preventative effect against mildew. This is a very common disease in tomatoes. Tomato plants and basil also complement each other very well in terms of growth habit. The basil covers the ground at the feet of the tall tomato plant.
Our tip: Parsley works just as well as basil in a mixed culture with tomatoes. Tagetes is also suitable for tomato beds, as it keeps nematodes and some diseases at bay.
Examples for Your Planting Plan With Tomatoes
We prepared some planting plans with tomatoes for you. You can easily copy the plans in your garden and work on it with our Fryd App.
The Milpa Bed: Mixed Crop of Corn, Beans & Pumpkin
The milpa, also known as the Aztec bed or Indian bed, is a mixed crop with beans, corn and pumpkin. As an alternative to beans, you can also choose other legumes such as peas. Instead of corn, tomatoes also work well as a climbing aid for the beans. You can also replace the pumpkin with other pumpkin plants such as zucchinis, melons or the nightshade plant potato.
Our tip: If you choose potatoes, tomatoes are not good neighbors, as both are susceptible to late blight. Corn would be a better planting neighbor here.
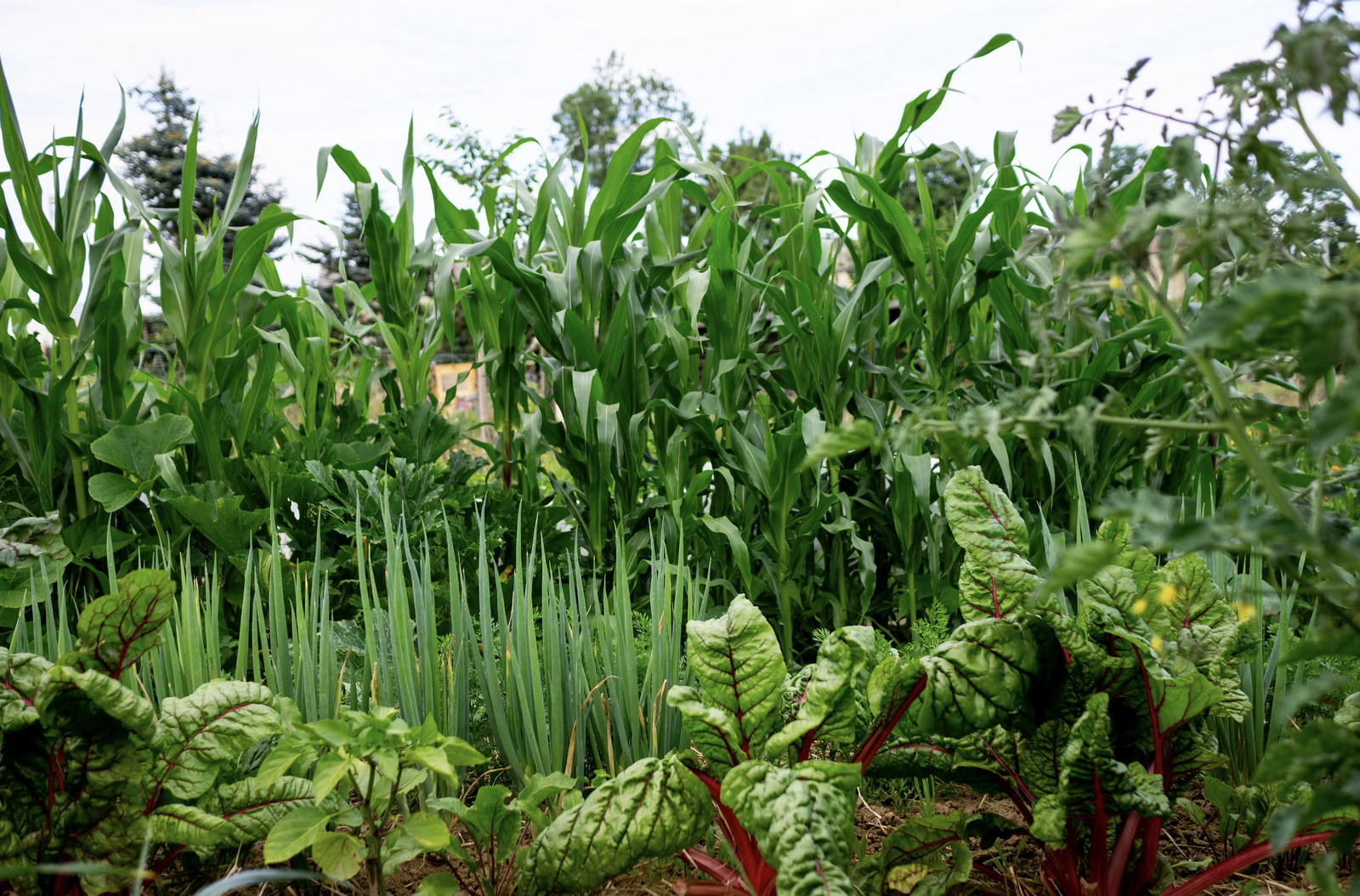

Milpa Planting Plan: Ideas & Examples
Carrots and Onions in a Mixed Crop
Carrots and onions are generally known as good neighbors. And for good reason: carrots keep onion flies away and onions keep carrot flies away. In this way, they naturally keep pests away from each other. However, carrots and onions have one crucial difference: both have different water requirements. While carrots like to be evenly moist, onions like to have dry feet. Soil that is too moist tends to increase the risk of rotting.
Our tip: Leek is also a bulbous plant and keeps carrot flies away with its scent. Leeks also like to be evenly moist. Leeks are therefore better suited as a neighbor for carrots. It also has a large root system, which loosens up the soil. This benefits the development of the carrots.
Mixed Culture With Cucumbers, Dill and Borage
This mixed crop is particularly versatile. These three plants not only complement each other well in the kitchen, but also in a mixed crop. The flowering borage also provides food for the insects in your garden. It attracts pollinators. Borage is also a medicinal plant and has an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect. Dill is also a very useful herb for mixed cultivation. It increases the germination capacity of cucumber seeds. This is an advantage for some seeds with a lower germination capacity, such as cucumbers, pumpkins and carrots. It is also said to improve the growth of cucumbers and their flavor.
Our tip: Onion plants are also very suitable for cucumber beds. They keep pests such as whitefly away with their essential oils.
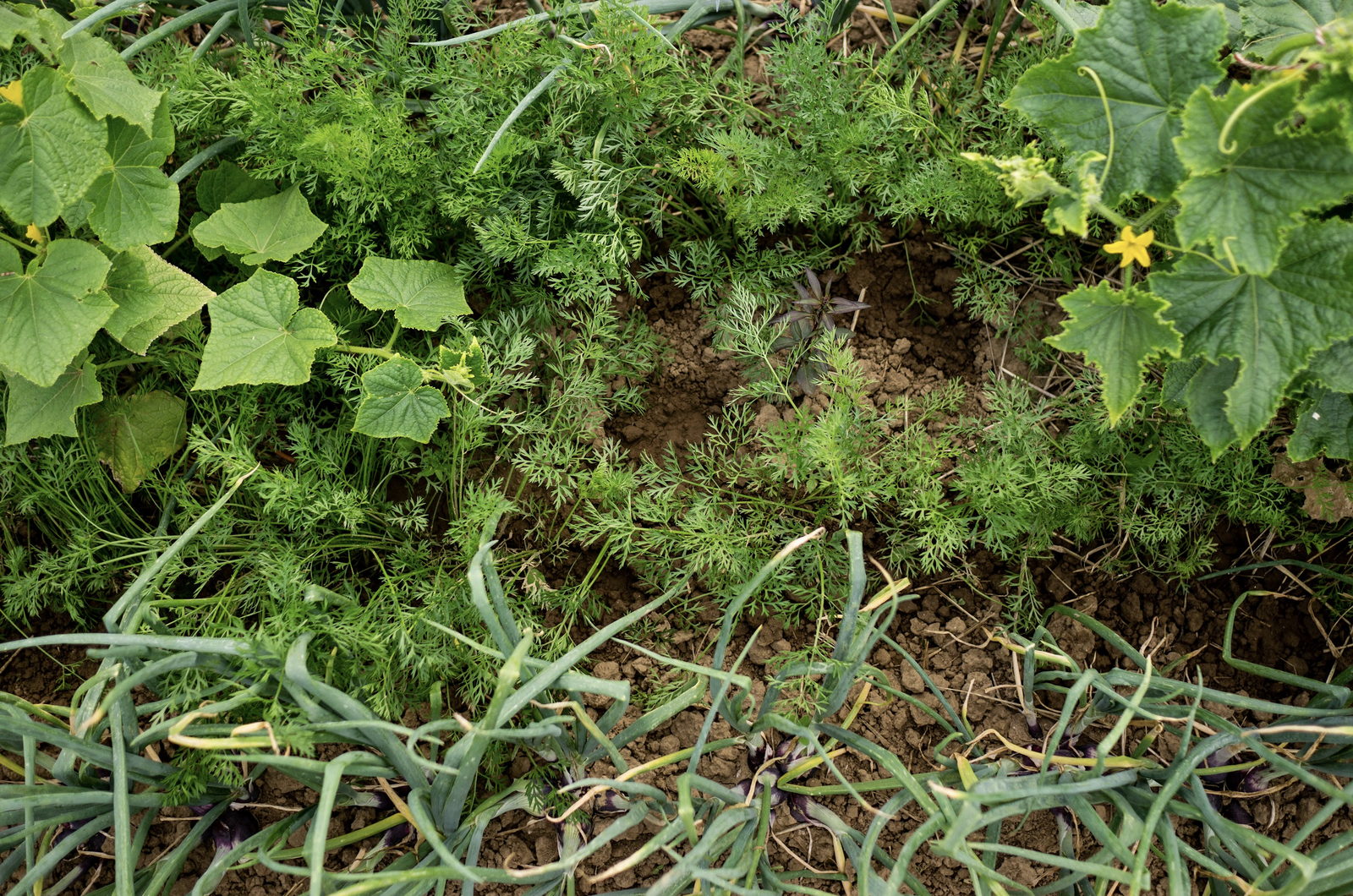

Ideas for Your Companion Cropping With Cucumbers
Strawberries and Onions: Companion Plants for Strawberries
Onion plants such as garlic, onions, leeks and chives keep slugs away with their smell. They also keep fungal spores away from the strawberries.
Our tip: Flowers are also good neighbors for strawberries. Borage is also a wonderful addition to the strawberry patch as it attracts pollinators. This encourages strawberries to set fruit. The same goes for marigolds, which also keep nematodes away with their roots.
Want to get helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds in the best possible way? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - your digital bed planner
Marie
Current Topics in the Community
05 March 2026
@Testi
Show 1 answer@tomatestabtomate
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation
FAQ
Mixed cultivation is a cultivation method in which different plant species are combined in such a way that they have a positive effect on each other, protect the soil and naturally keep pests away.
What are the advantages of mixed cultivation?
It helps to maintain soil fertility, makes optimum use of the space in the vegetable patch, increases diversity in the garden, attracts beneficial insects and keeps pests away.
What are examples of typical mixed crops?
Some popular examples are tomatoes with basil or parsley, corn with beans and pumpkin, and cucumbers with dill and borage.
Where can I find a mixed culture table to print out?
In this article you will find a mixed crop table as a free download, which shows you good and bad plant neighborhoods and makes it easier for you to plan your mixed crop.