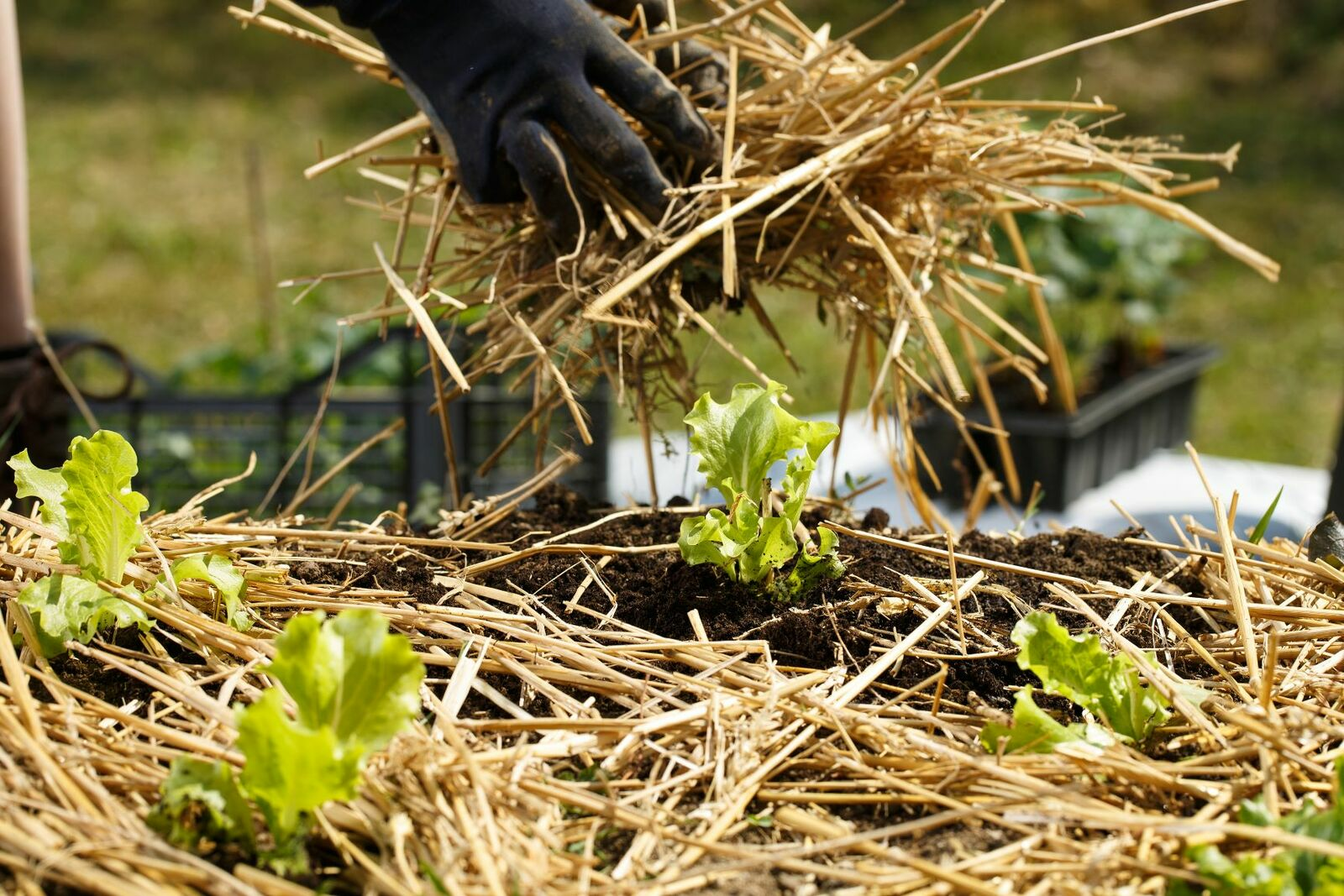

Garden Mulch: Types of Organic Mulch
Mulching is the application of a soil-covering layer to a field or bed. This can be in the form of dead plant material (straw, grass clippings, wood chips, bark mulch, etc.) or living plants, which is called living mulch. Plastic sheeting can also be used as mulch. Everything you need to know about mulching your vegetable garden can be found here.
This Article Contains:
Quick Overview
What Is Mulch & What Does Mulch Do?
- Mulching involves layering organic material such as straw, hay or bark mulch on top of the garden soil.
- Mulching has many advantages: Erosion protection, weed suppression, fertilizer, evaporation protection and therefore less water consumption, soil improvement,...
Types of Mulch Materials: Straw & Co.
- Grass cuttings and herbs such as nettle or comfrey
- Leaves, straw or hay
- Cardboard or cardboard (especially for weed suppression)
- Bark mulch
- compost
- Plastic sheeting (especially for stubborn and persistent weeds)
- Live mulch or green manure
What Is Mulching?
Mulch is a layer used to cover a bed. This layer can be made of organic material such as hay, grass clippings, straw, leaves or wood chips, but it can also be made of plastic. However, this film or woven mulch is used primarily in commercial vegetable production. Live mulch/undercutting is also possible, in which lower growing plants are planted under the higher growing plants, covering the soil like a living carpet of plants. Mulching is used by many knowledgeable gardeners because of its many benefits. Mulching is also an important tool in a Permaculture Garden or in the No Dig Method for maintaining soil functions.
What Is Mulch Used For?
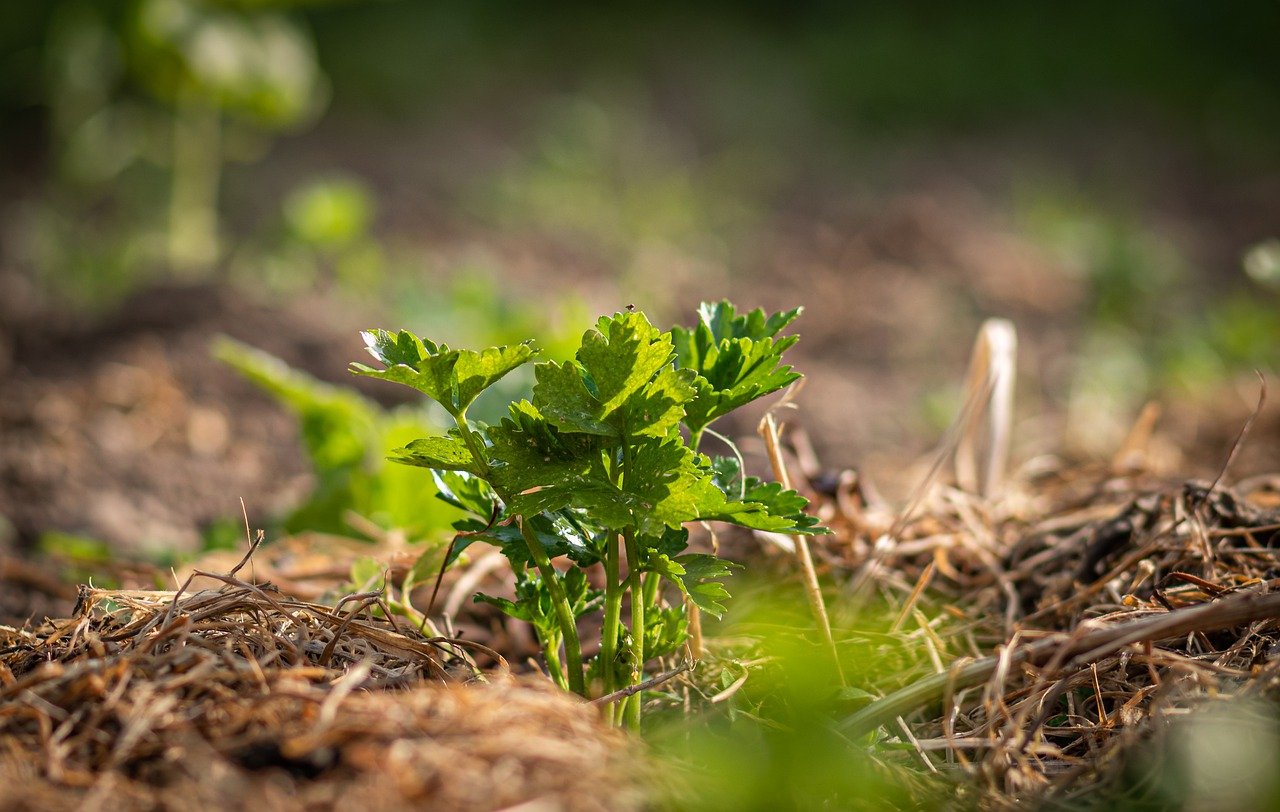

Next, it is important to understand what functions mulch performs in the garden. First, it protects the soil. Between rows or between individual plants with a large gap between them, the soil is often exposed like an open wound and therefore susceptible to erosion. A layer of mulch protects the soil from erosion during heavy rain or wind. When you use organic mulch, you also provide a "food supply" for soil organisms, which gradually convert the mulch into humus, improving soil quality, loosening the soil, and making nutrients available to plants. Many soil organisms are also sensitive to light and enjoy the dark and moist environment that mulch creates at the soil surface. And that brings us to the next benefit of mulch: If you mulch your bed well, you will need to water much less. Mulching protects the soil from drying out when it is not directly exposed to sun and wind. But reduced watering is not the only effect that saves you labor. Mulch also prevents weeds from settling or growing in your bed and "stealing" important nutrients and light from your plants. And as every gardener knows, less weeds means less backache. Finally, mulch provides certain plants, such as strawberries, with a soft, dry bed on which to set their fruit. This better protects them from dirt and mold. As you can see, mulching has many benefits for us as gardeners. To learn more about how your garden soil works and what soil organisms there are, take a look here.
Organic & Natural Mulch: Choose the Right Materials
The most important factor when it comes to mulching is choosing the right material, as not every material is equally suitable for the various mulching applications.
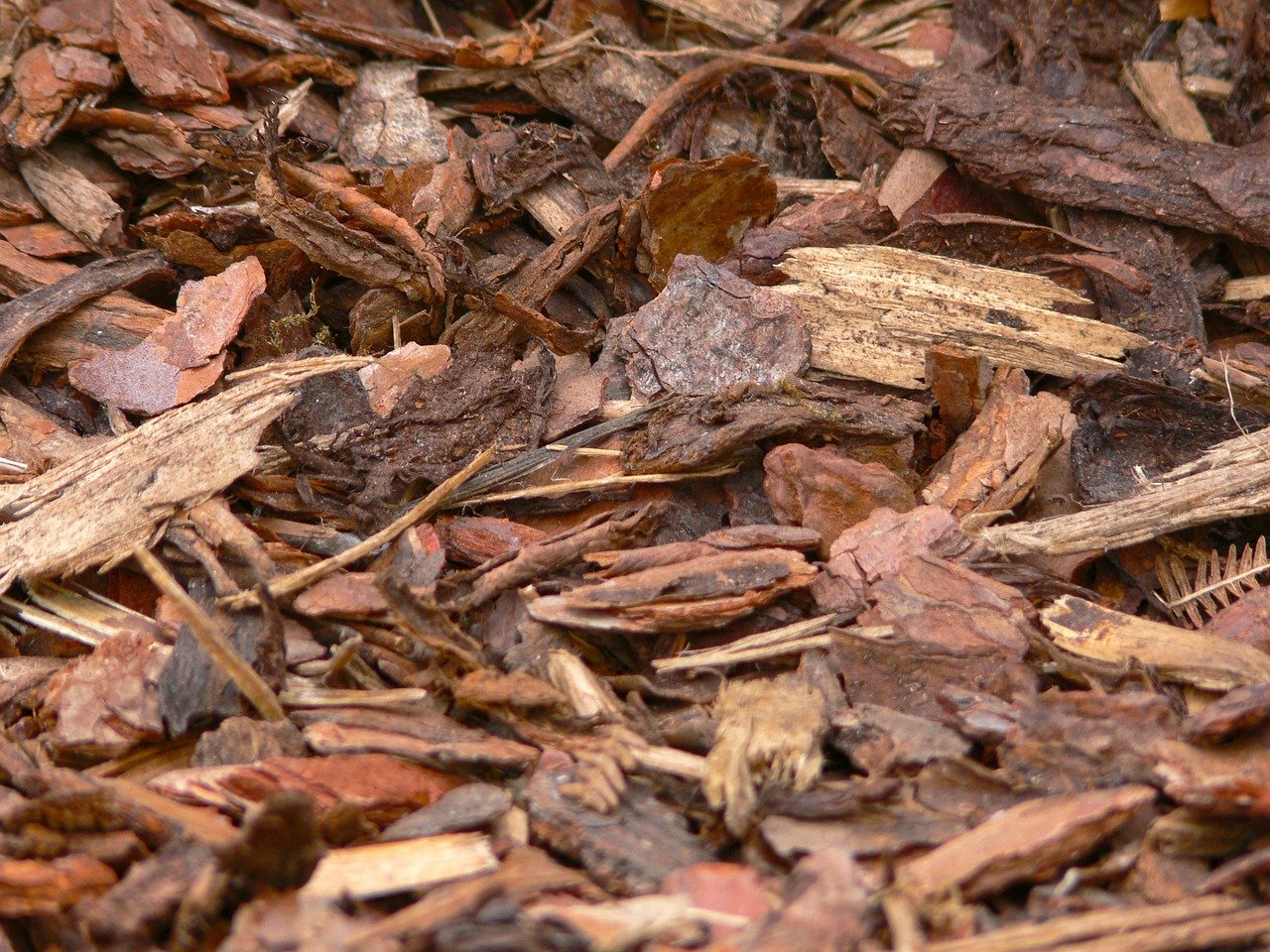

Mulching With Straw, Compost, Hay and Co.
When it comes to improving soil quality, you want to make sure that the carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) of the mulch is not too high. If the C/N ratio is high, that is, if the mulch contains much more carbon than nitrogen, soil organisms will extract nitrogen from the soil as they convert the mulch into humus. This nitrogen is then unavailable to your plants. Materials with a high C/N ratio include straw and wood. These materials should be used for no more than one season on nutrient-rich soils; on nutrient-poor soils, they should be avoided altogether. Instead, use compost, hay, leaves, or fresh grass clippings, which contain relatively more nitrogen and help improve soil quality. However, these fresher mulches can increase the risk of fungal diseases, such as mold or mildew, especially in wet weather. So if you live in rain-prone areas or grow vegetables that are susceptible to fungal diseases, you may want to use straw. Another application for which straw is well suited is the protection of fruits that lie on the soil surface, such as strawberries or pumpkins. Due to its high C/N ratio, straw remains stable as mulch for a long time, providing a relatively clean surface for your fruit.
Share Ideas With Other Gardeners!
To exchange ideas with other gardeners and benefit from the experiences of others, you can visit our Fryd community. Here you will also find tips on mulching.
Join Community NowOverview of types of mulch
Here is a brief overview so that you know when it is best to use which materials and which plants tolerate bark mulch.
Herbs and Grass Cuttings for Mulching
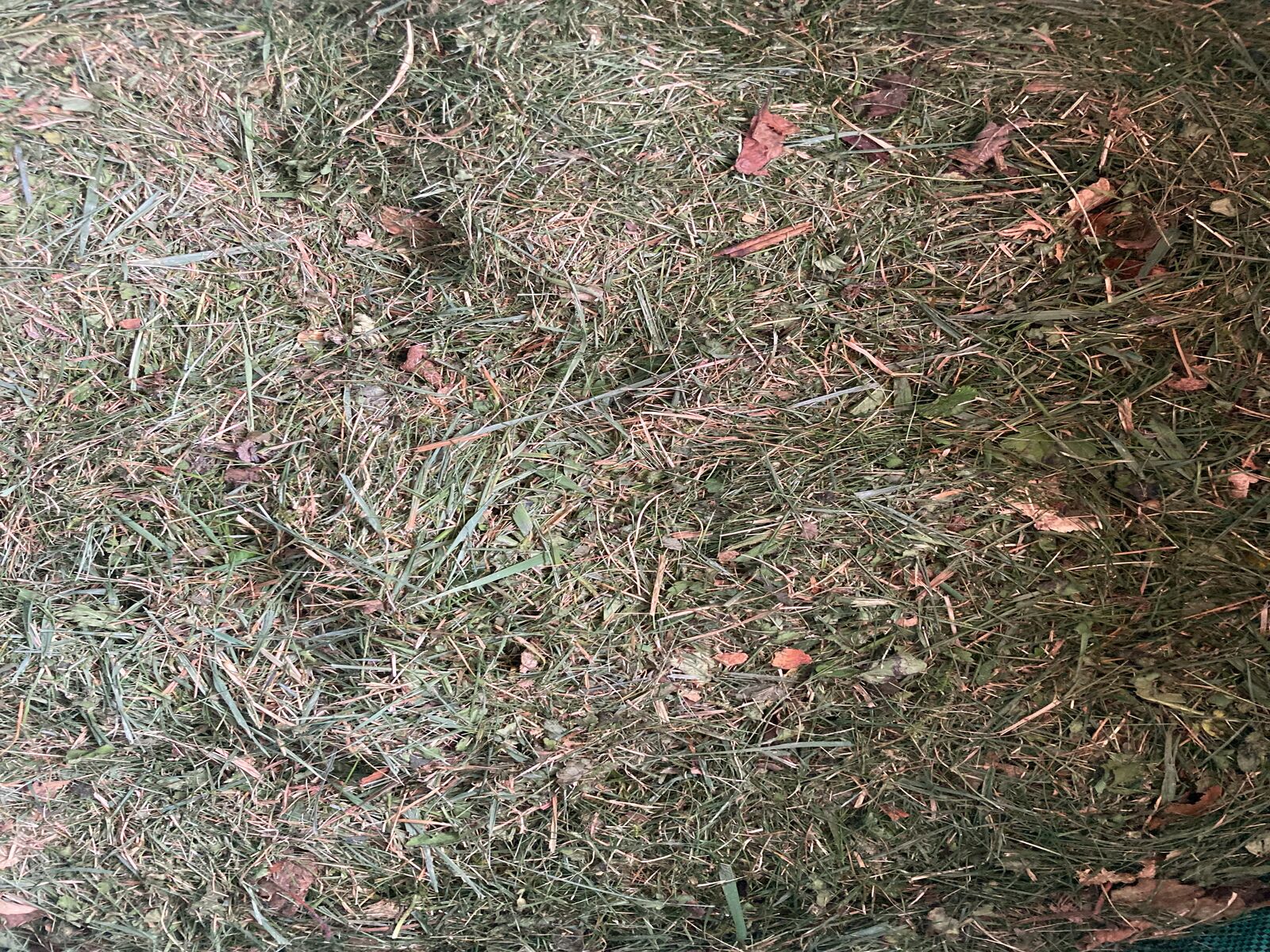

- Grass cuttings: Before the grasses flower, suitable for almost all beds. Only spread a thin layer, otherwise air can no longer reach the soil. In damp spring or fall, however, grass clippings can encourage the spread of fungal diseases.
- Weeds: Before flowering, weeds can be pulled out and chopped up on the spot. The roots should be exposed or removed so that they cannot grow again.
- Nettles: Nettles are often only seen as weeds, but they can be very useful as manure for fertilizing or as indicator plants for nitrogen-rich soils. Their leaves contain a lot of nitrogen, which is why they provide the soil with additional nutrients when used as mulch. They are therefore ideal as mulch for nutrient-poor soils.
- Comfrey leaves: They contain a lot of potassium, which serves as a nutrient for your vegetable plants. This special mulch is therefore particularly suitable for crops such as tomatoes, which need a lot of potassium.
In any case, you should make sure that your mulch does not contain any weed seeds. Grass cuttings are therefore only suitable if there are no flowering plants growing in the meadow. Even uprooted weeds should only be mulched if they do not carry seeds. Otherwise, the weed-suppressing effect will be null and void and you won't be able to enjoy the bed on which you have just spread the weed seeds for many years to come.
Leaves and Straw as Mulch
Straw is mainly used to suppress weeds or to protect strawberries from moisture. Straw as mulch does not fertilize, but decomposes very slowly, releasing nutrients only gradually. Straw can be used on moist soils in particular.
Leaves can be used as a mulch layer, especially under trees and shrubs. Strawberries can also be cultivated with leaves as mulch. Leaves often slightly acidify the soil, which is ideal for strawberries.
Cardboard or Paperboard Against Weeds
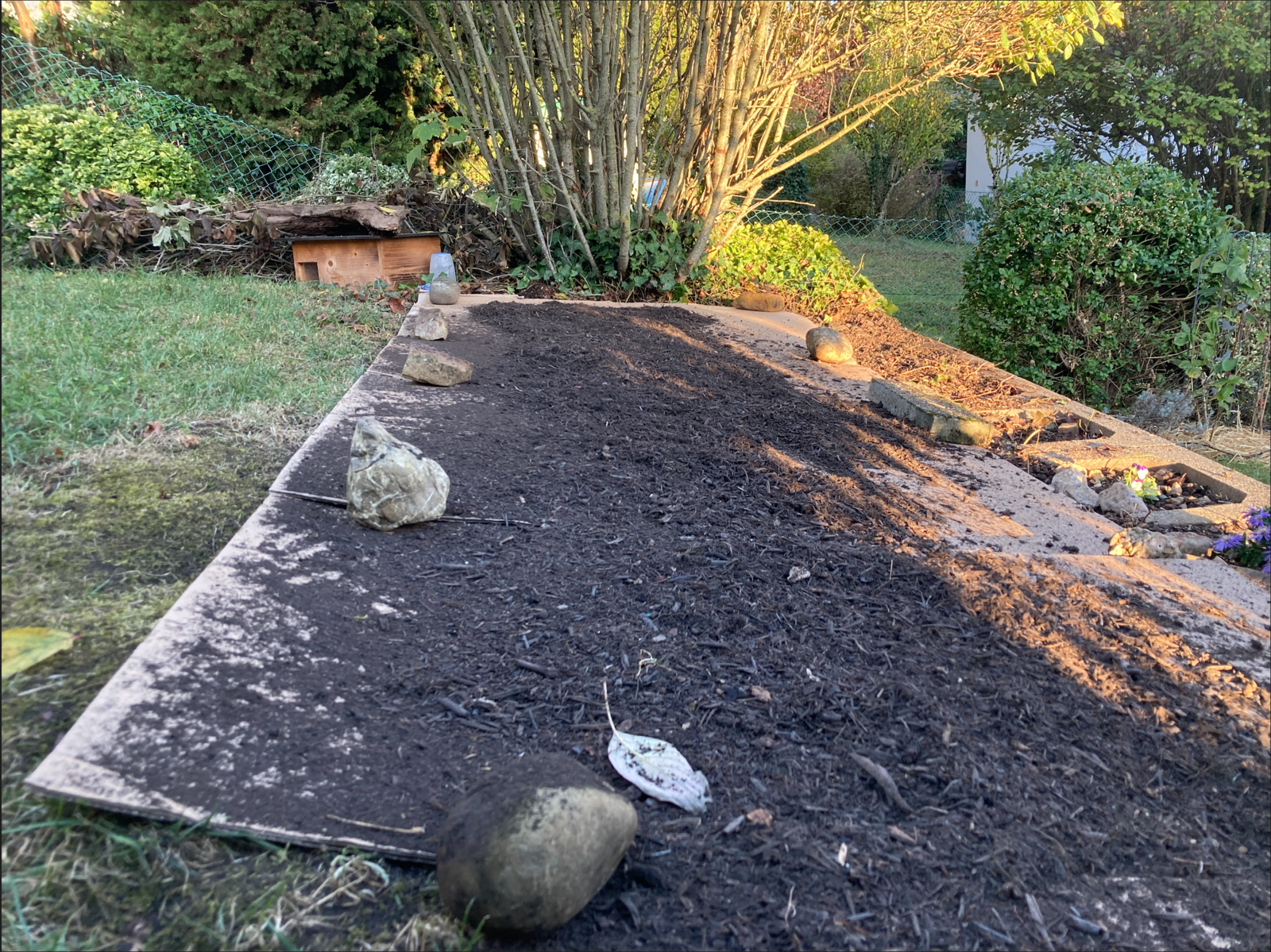

Can be used in almost all beds. Make sure that the materials are unprinted so that no heavy metals contained in the printing ink are introduced into the soil. Moisten the cardboard at the beginning and cover the edges with stones so that nothing flies away in the wind. Cardboard is also used as mulch material for sheet mulching.
Bark Mulch Against Weeds: Paths or Under Trees and Shrubs
Bark mulch and wood shavings are well suited for flowering shrubs or berry bushes. This mulch material is rather unsuitable for flower beds, as the material decomposes very slowly and therefore releases fewer nutrients. However, bark mulch and wood shavings can be used to create small paths in your bed. Alternatively, you can also spread compost on your paths to suppress weeds. This is part of Charles Dowding's no-dig method. The compost preserves the soil structure and suppresses weeds.
Compost as Mulch and Fertilizer
Compost is also a good mulch and serves as a great fertilizer for the soil. Especially with the no-dig method, compost is used to improve the soil and maintain the soil structure. Charles Dowding recommends a layer of compost about 2.5 cm thick to fertilize no-dig beds for the season . If you do not have no-dig beds, you may need more compost to fertilize and improve the soil, depending on the soil. Charles Dowding recommends up to 15 cm of compost on lean soils.
In addition, compost can also suppress most weeds. However, some perennial weeds are a little more stubborn, and you can use cardboard, cardboard or black plastic sheeting to suppress weeds.
Mulching With Plastic Films
Mulch made from plastic film or fabric is suitable for suppressing weeds and protecting the soil from erosion and drying out. They also protect fruit close to the ground from spoiling. However, they do not contribute directly to humus formation and do not look very attractive in the garden. Furthermore, the wear and tear of non-biodegradable films also leads to the entry of microplastics over time, so make sure to remove the films completely after use. However, if you have a piece of land with particularly stubborn weeds such as couch grass (Elymus repens) or field bindweed (Convolvulus arvensis), such a film can help you to make the area usable for vegetable cultivation. You can also cut small holes in the film and plant the area. One advantage of black film is that it warms up quickly, which is an advantage for heat-loving plants such as watermelons or pumpkins.
Green Manure and Ground Cover
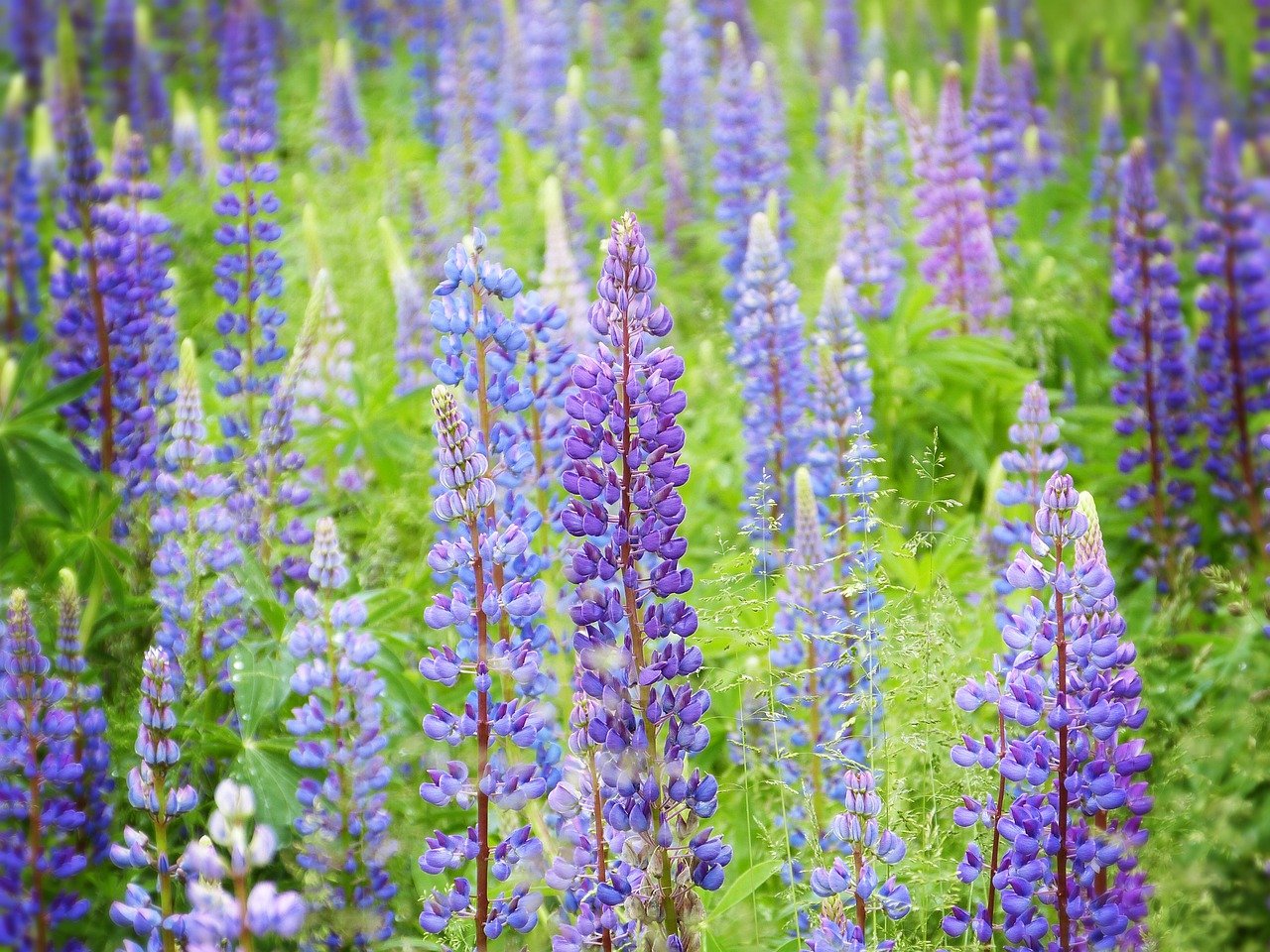

For example, you can use green manure mixtures as a living plant carpet. Mustard seeds or legumes first cover the soil as living plants and can also serve as dead organic ground cover after mowing. Green Manure protects the soil from evaporation and weed growth. The green manure plants loosen the soil with their roots and, as legumes, can even enrich the soil with nitrogen, which serves as a nutrient for plants.
How to Mulch Correctly
Last but not least, it remains to be clarified how best to mulch. Above all, you should make sure that the mulch layer is the right thickness . Basically, the thicker it is, the better the weed suppression and water saving. However, lush, fresh plant material such as grass clippings or weed cuttings should not be applied too thickly, otherwise oxygen will no longer reach the soil. Both soil organisms and plant roots need oxygen. If this is lacking, they cannot continue to grow and die. In addition, the mulch layer can only decompose if there is sufficient oxygen. Otherwise it can lead to rotting. Therefore: It is best to only spread pre-dried material loosely and no more than 10 cm thick. Water your mulch once after you have applied it so that it immediately provides optimum protection for the soil and does not soak up water from the soil first.
All in all, mulch is one of the simplest but most effective ways to save you work in the garden: You have to water less, weed less, your soil becomes more fertile by itself and let's be honest, a properly mulched bed also just looks nice.
We hope you now know everything you need to know about mulching. If you have any questions or comments, please write to us at [email protected] or share your experiences with us on social media. To make sure you don't miss any more articles, follow us on Instagram and Facebook or sign up directly for our newsletter.
Want to get helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds in the best possible way? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - Your digital bed planner
Source: Charles Dowding, #No Dig, 2023, Munich: Dorling Kindersley Verlag GmbH
Isabell
Current Topics in the Community
05 March 2026
@Testi
Show 1 answer@tomatestabtomate
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation
FAQ
What is mulch and what is mulch used for?
Mulching refers to the application of a protective layer of materials such as straw, grass clippings, wood chippings, bark mulch or living plants to the soil. It offers numerous benefits such as erosion control, weed suppression, nutrient supply, evaporation protection, improvement of soil structure and crop protection.
Which types of mulch materials are suitable?
Suitable mulching materials include straw, compost, hay, leaves, grass cuttings, nettles, comfrey leaves, cardboard, bark mulch and plastic sheeting. The choice depends on factors such as soil quality, moisture and specific garden needs.
Mulch helps to improve soil quality by enriching the soil with nutrients, loosening the soil structure and creating a favorable environment for soil organisms. Organic mulch is gradually broken down into humus, which nourishes the soil.
What is green manure and how is it used?
Green manure are plants used to cover the soil. It is used to protect the soil, retain moisture and suppress weed growth. Examples are green manure mixtures such as lupins or mustard seed.