
Plant Strengtheners: Preventive Plant Protection Without Chemicals
For your plants to be strong enough to fend off diseases and so-called pests, they need to be healthy. Gardeners can help their protégés stay healthy for longer using natural means without chemicals. There are several ways to do this, such as plant juices, plant teas and plant decoctions as well as rock flour or horn meal. All of these products strengthen the immune system of your plants and are therefore known as plant tonics. You can find an overview and further information on this topic here.
This Article Contains:
Quick Overview
Strengthen Plants With Plant Tonics
- are intended to improve plant health
- organic plant strengthening agents: plant juices, teas, decoctions, effective microorganisms
- inorganic agents: rock flour and lime
- different modes of action depending on the starting material and production method
Tips for Use in the Garden
- spray as foliar fertilizer every 7 to 14 days
- apply in a dry, rain-free period
- additional crop protection measures
Preventive Plant Protection With Plant Strengtheners
Plant strengthening agents include, for example:
- Plant Infusions
- Plant Teas & Brews
- Compost Tea and Bokashi Ferment
- Horn meal
- Rock Flour and Lime
Plant tonics are primarily intended to improve plant health. Plant tonics and the like help you to strengthen your plants naturally and thus prevent diseases and other pathogens. However, these preparations cannot be used to combat diseases afterwards, i.e. when your plants are already sick, or only to a limited extent (depending on the severity of the infestation). For example, if you have a zucchini infested with mildew, you can only remove the diseased leaves and dispose of them in the household waste. If there are still enough leaves left, you can treat the plant with Nettle Manure or Horsetail Tea. Then all that remains is to hope that it has survived the procedure.
These products are mainly used in organic gardening. In addition to other crop protection measures such as pheromone traps or yellow boards, they are another measure to protect your plants from infestation. Below you will find an overview of various plant strengthening agents. You can also easily make some of them yourself!
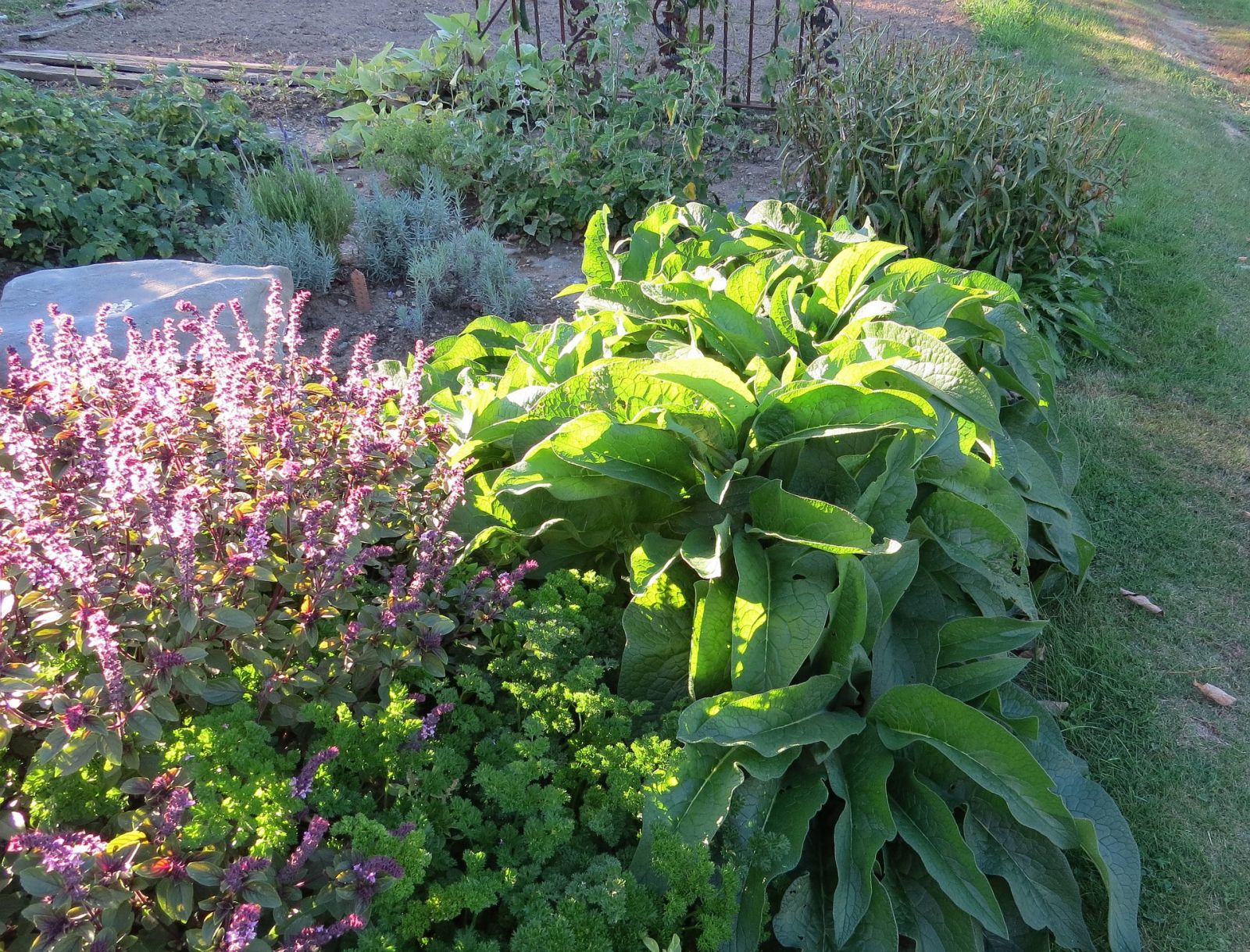

Plant Juices, Teas and Decoctions Made From Wild Herbs
Some wild herbs that can be found in most gardens can be used as plant extracts to strengthen your crops. This is a great way to return garden waste to the cycle. This is because you can easily make plant juices, teas or decoctions from them. In addition to extracts from plants, extracts from compost such as compost tea or algae are also possible. For the home garden, organic-based products are particularly easy to make yourself. Each plant extract has its own mode of action, depending on the ingredients of the plants used and the method of production.
What Is the Difference Between Slurries and Brews/Teas?
Plant ferments such as nettle manure are produced by fermenting the plant material under low-oxygen conditions. This mainly breaks down carbon and enriches other nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus. This is what makes plant manure such a good fertilizer. In addition, effective microorganisms are involved in the fermentation process, which in turn has a positive effect on soil and plant health. The nutrients are also very easy for the plants to absorb, which is why foliar fertilization (spraying/spraying diluted liquid manure on the leaves) can be very effective. However, due to the acidic pH value of liquid manures, they must always be diluted with water!
Plant teas and decoctions are infused with warm water. Only water-soluble plant substances are dissolved. One disadvantage of plant teas and plant decoctions is that they do not keep for long and should therefore be used up after three days at the latest. In addition, unlike plant ferments and infusions, they lack some nutrients and effective microorganisms. In a tea or brew, mainly flavonoids, tannins and easily soluble aromas are released. Plant teas and brews are therefore less suitable as fertilizers, but are mainly used to strengthen plants!
Making and Using Plant Tonics Yourself - A Comparison
| Procedure | Manufacture | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Water Extract | place chopped plant parts in water for 1 - 3 days and then sieve | undiluted or diluted 1:1 for defence against pests and for soil care |
| Brew | like cold water extract, only boil for 15 - 30 minutes after soaking and then sieve | undiluted for pest defence and soil care |
| Tea | brew the plant parts with hot water and leave to infuse for 15 - 20 minutes, allow to cool and strain. | 1:10 preventive plant protection and 1:20 as foliar fertilisation |
| Plant Slurry | ferment plant parts for 2 - 3 weeks | 1:20 as soil fertilisation and 1:50 as foliar fertilisation |
Effective Microorganisms: Little Helpers to Strengthen Plants
Among the organic preparations there are some products with effective microorganisms. These preparations usually contain bacteria and/or fungi. Foliar fertilization increases the resistance of the plants. Microorganisms that are beneficial and "good" for the plant displace pathogens on the plant surface. In addition, new pathogens find it difficult to colonize the plant. Preparations with effective microorganisms are created, for example, by fermentation of plant parts or compost. An easy way to make your own effective microorganisms at home is to use a Bokashi Bucket. Alternatively, you can also brew a compost tea. This is also rich in microorganisms.
Rock Flours and Limes
Plant strengthening agents of mineral origin such as rock powders and limes usually have a high silicon content. This naturally increases the resistance of the leaves. This makes the plant more resistant to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew. However, these two agents are not only used to strengthen plants, but also to improve and maintain the soil. This means that these agents have a direct and indirect positive effect on your crops.
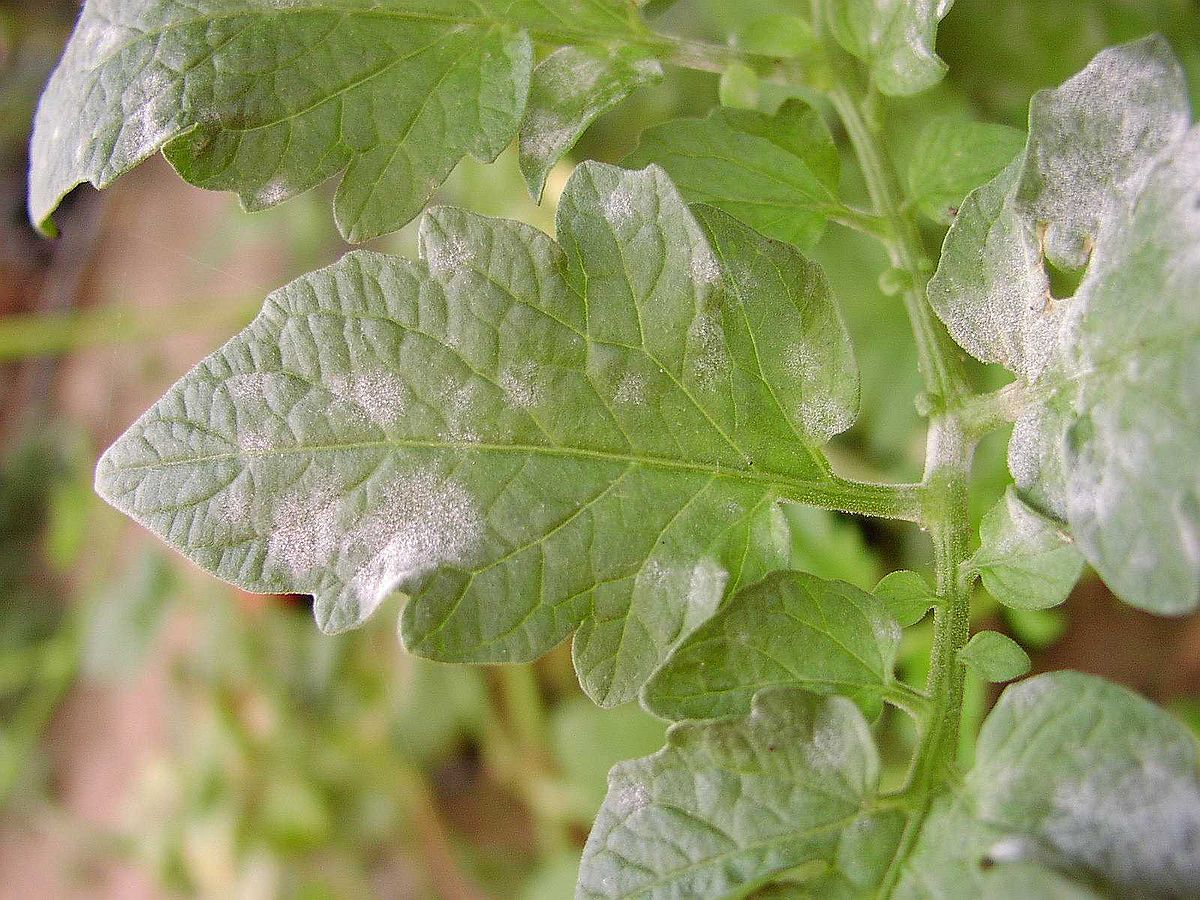

Tips for Using Plant Strengtheners in the Garden
- Plant strengthening agents are often sprayed on the leaves as a foliar fertilizer diluted with rainwater. This allows the active ingredients to reach the plant more quickly and strengthen it directly.
- For foliar fertilization, the weather over the next few days should be dry and rain-free. Otherwise the agent may be washed off by the rain before it can take effect.
- As these products are primarily preventative, you must apply them regularly to your plants. Repeat the treatment every 7 to 14 days, depending on the crop.
- You should experiment a little with the different extracts. Plant tonics do not work equally well everywhere and with every plant. Bear in mind that the effect also depends on other factors such as weather conditions, growing conditions and water and nutrient supply.
- The effect is particularly noticeable in plants that are not yet particularly healthy and are already a little weak. Nevertheless, even robust plants can be better protected with plant strengthening agents. There may be fewer visible changes, but they support plant immunity.
- In the event of an impending infestation, these products help to keep your plants healthy for longer. However, you should take additional measures and install crop protection nets, yellow boards or pheromone traps. In organic farming, it is a combination of many regulating measures that protect your crops. You can find more Tips and Tricks on Preventive Plant Protection in our article on the subject.
- Depending on the product, plant strengthening agents also contain nutrients and, depending on the method of production, effective microorganisms. In addition to foliar fertilization, you can also apply them to the soil to boost biological activity on the one hand and fertilize plant-available nutrients on the other. You can read more about Ecological and Organic Fertilization in our article on the subject.
- To get your compost going and promote composting, you can inoculate it with preparations containing effective microorganisms.
If you have any questions or comments, please write to us at [email protected].
Would you like to receive helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds optimally? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - your digital bed planner
Marie
Current Topics in the Community
05 March 2026
@Testi
Show 1 answer@tomatestabtomate
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation
FAQ
Plant tonics are natural preparations that improve the health of plants by strengthening their immune system and making them more resistant to diseases and pests.
Can you make your own plant tonics?
Yes, there are various recipes and methods for producing plant tonics from organic materials such as plant juices, teas and decoctions, as well as from inorganic materials such as rock flour.
How do you apply plant strengthening agents correctly?
Application varies depending on the product, but often involves spraying diluted solutions directly onto the leaves or soil to strengthen and nourish the plants.
What are the benefits of plant strengtheners?
They offer an ecological alternative to chemical pesticides by strengthening plants in a natural way and helping to promote a healthy and sustainable garden.
Which plants are suitable for the production of plant tonics?
Many wild herbs and garden waste can be used to produce useful plant extracts that serve as natural plant tonics.