
Methods of Preserving Vegetables and Fruits
Without sufficient preservation, fruit and vegetable stocks are quickly colonized by microorganisms such as fungi and bacteria and spoil. There are various methods of containing the growth of these microorganisms and thus preserving fresh food. In this article, I will briefly introduce you to the most common methods of preserving food.
This Article Contains:
- Preserving in the Oven or Pot: Preserving Pears, Cherries & Co.
- What Can You Preserve?
- Preserving in a Pot: Tips for Preserving
- What Can You Boil Down?
- Preserving Fruit With Jam
- Fermenting Vegetables: How It Works
- Fermenting Vegetables: A Recipe for Beginners
- Drying Fruit, Vegetables, Mushrooms & Herbs: In the Air or in the Oven
- Checklist & Tips: Preserving Fruit & Vegetables
- Frequently Asked Questions About Preserving
Quick Overview
Preserving and preserving fruit and vegetables for a long time:
- Preserving in the oven or pot: heat fruit and vegetables in a preserving pot to 75 to 100 ° C/167 to 212 ° F for about 2 hours, when preserving start with the oven at lower temperatures
- shelf life: at least 1 year
- Preserving in a pot: boil fruit or vegetables with sugar, salt or vinegar for about 10 minutes and pour directly into clean jars while hot
- shelf life: 6 to 12 months
- Making jam and preserving fruit: preserve fresh fruit with sugar, apple pectin or agar agar
- shelf life: 6 to 12 months
- Fermenting vegetables: raw vegetables are cut, mashed and mixed with salt. The whole thing must now ferment for some time, depending on the vegetable or fruit (between 1 and 9 weeks).
- shelf life: at least 1 year
- Drying fruit, vegetables, herbs and mushrooms: simply dry in a dehydrator, oven or simply leave to air dry and sprinkle with salt or sugar if necessary.
- shelf life: at least 1 year
Preserving in the Oven or Pot: Preserving Pears, Cherries & Co.
Preserving is a very energy-saving method of preserving food, as energy is only required once. The desired fruit or vegetables are filled into jars and then heated in a preserving pot at temperatures between 75 to 100 °C /167 to 212 ° F for up to 120 minutes. During this time, water vapor and hot air escape and the jar closes airtight when it cools - creating a vacuum. As an alternative to the pot, you can also preserve in the oven, which works in the same way as in the pot. Just be careful not to set the oven too hot and start at a lower temperature.
- suitable are: Pre-cooked vegetables, sauces, fruit purée, etc.
- you will need: Preserving jars with rubber ring
- shelf life: At least one year
What Can You Preserve?
| Fruits | Vegetables | Other Foods |
|---|---|---|
| apples | beetroot | fish |
| apricots | cabbage | fruit juices |
| berries | carrots | jams |
| figs | courgettes | meat and poultry |
| grapes | cucumbers | pickled vegetables |
| peaches | peas | salsa and relish |
| pears | peppers | sauerkraut and other fermented foods |
| plums | tomatoes | soups and stews |
| quinces | beans |
Preserving in a Pot: Tips for Preserving
Alternatively, pre-cooked vegetables, tomato sauces or chutneys can also be filled directly hot into boiled jars. This method is very simple and takes very little time. The fruit or vegetable in question is boiled with sugar, salt or vinegar for approx. 5 - 10 minutes and then quickly poured into fresh jars. If the vegetables in the jar are not completely covered with liquid, you can prepare a stock with salt and vinegar, pour this hot over the cooked vegetables and then seal the jar airtight. The whole thing can then be kept for between 6 and 12 months.

What Can You Boil Down?
- fruit as jam, jelly, compote or whole fruit, such as apples, pears, cherries, mirabelle plums, plums, peaches,...
- vegetables such as beans, cucumbers, beet, tomatoes, zucchinis,...
- fish, meat and poultry, if properly prepared and cooked in a pressure disposable pot
- soups, stews, sauces and relish
- pickles and other pickled vegetables
Tip: When cooking protein-rich fruit, a lot of foam forms, which should be skimmed off the surface as it reduces the shelf life. A little butter slows down the foaming.
Leafy vegetables, pasta and rice, for example, arenot suitable for preserving as these foods lose their texture and become mushy. Broccoli, cauliflower and other cruciferous vegetables are also unsuitable as they tend to develop an unpleasant taste. In addition, dairy products and eggs are also not good for canning due to the high risk of spoilage. If your stew or soup is thick, it is better to use another option, as the heat often cannot penetrate evenly. You should take special care when preserving mushrooms, but it is possible.
Preserving Fruit With Jam

The preparation of jam works on the same principle, only sugar is added to fresh fruit. The sugar binds the freely available water in the fruit and thus inhibits the microorganisms. Heating has an additional preservative effect. Pectin-rich fruits such as apples, quinces, currants and gooseberries can gel on their own. However, additional gelling agents can also be used to achieve the desired consistency.
- vegan gelling agents: apple pectin, agar agar (from algae)
Would You Like More Tips?
To exchange ideas with other gardeners and benefit from the experiences of others, you can visit our Fryd community. There are many experienced gardeners here who can give you tips on preserving vegetables!
Become Part of the Community NowFermenting Vegetables: How It Works
Sauerkraut and green beans are traditionally preserved by spontaneous lactic acid fermentation. To do this, the raw, clean vegetables are finely chopped, salted and tamped in a container for fermentation until liquid is released. The vegetables should be completely covered with liquid; if the vegetables' own juice is not sufficient, a little cooled brine (20-30 g/L or 0,7 fl. oz./2,1 pt) can be added. The lactic acid bacteria do not need to be added separately, they are already present in the air and are introduced into the vegetables during mashing. During fermentation, the pH value drops, which means that the undesirable microorganisms cannot continue to grow and are displaced by the lactic acid bacteria. The salt also binds water and inhibits the growth of yeasts and molds.
Fermenting Vegetables: A Recipe for Beginners

You need approx. 20 - 30g/0,7 - 1,1 fl. oz. of salt per kilogram of vegetables. More salt is used for vegetables with a high water content, such as cucumbers, than for beet and carrots, for example. The screw-top jars should not be completely sealed so that any gases can escape. Leave the jars in a warm place for the next one to two weeks. During this time, a kitchen towel or similar should be placed underneath to catch any bubbling juices. Then move the jars to a cooler place (e.g. in the cellar); storage temperatures of 15 - 18 °C/59 to 64 °F are now ideal. The longer the ferment stands, the more aromatic it becomes. In principle, all vegetables are suitable except leafy vegetables such as spinach and lettuce, which become very slimy. The shelf life of fermented foods is at least six months.
How Long Does Fermentation Take?
| Water-Rich Vegetables | Fermented Cabbage | Root Vegetables |
|---|---|---|
| appr. 1 week | 4 to 6 weeks | 7 to 9 weeks |
Tips for Fermenting:
- Do not use iodized or fluorinated salt
- Do not close screw-top jars completely (risk of explosion!)
- Do not fill jars to the brim
Drying Fruit, Vegetables, Mushrooms & Herbs: In the Air or in the Oven
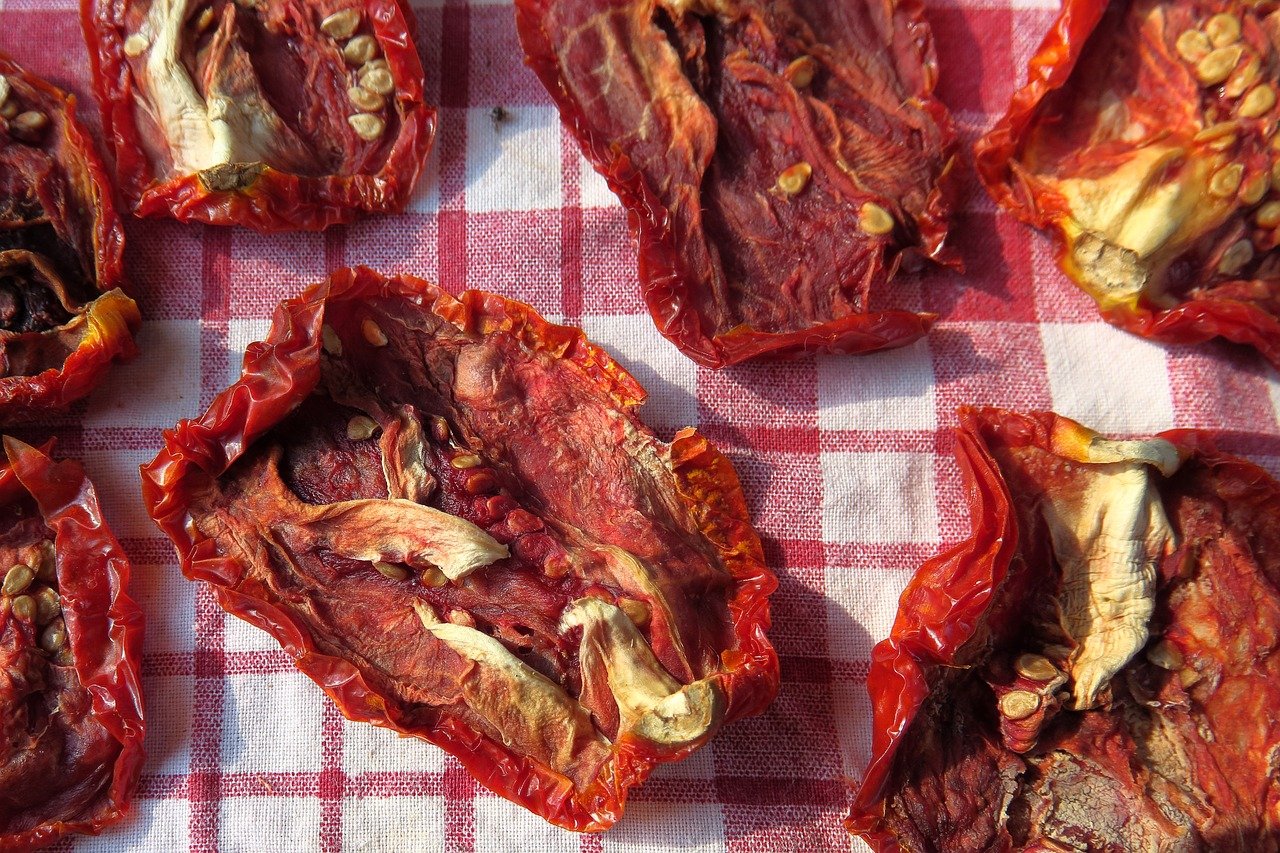

During the drying process, heat and air circulation remove the water contained in the food. From a residual moisture content of 8 - 20 %, microorganisms can no longer multiply and the food is preserved. Sugaring or salting increases the effect and turns dried tomatoes, for example, into a ready-made, tasty snack. In general, fruits with a high water content should be dried particularly carefully. Herbs, on the other hand, can simply be hung upside down or laid out on a dry kitchen towel.
- suitable are: fruit, vegetables, mushrooms, herbs
- important: careful storage
- methods: dehydrator, oven, in the sun & air
- tip : dried herbs, tomatoes, etc. are ideal for refining oils.
Checklist & Tips: Preserving Fruit & Vegetables
- Only use flawless ingredients: No fruit or vegetables with bruises, etc. - Use these directly.
- Season the ingredients with herbs, etc. as desired.
- Only use clean jars, lids and rubbers. It is best to place the jars in hot water for a few minutes to kill all germs. Then drain on a fresh kitchen towel and only turn over when filling. The gums should be cleaned with vinegar, not washing-up liquid. The knives and graters used should also be properly cleaned.
- Damaged lids and rubbers should not be used, as this can allow air to get into the food.

- Observe the preserving temperature and duration specified for the fruit or vegetable in question.
- The temperature of the water bath must always be the same as the jar contents at the start of the preserving process. Pre-cooked sauces, etc. are therefore placed in hot water, cold contents in cold water.
- After boiling down, the jars should be left in hot water for about 10 minutes. Then take them out of the pot and place a kitchen towel over them. This allows the jars to cool slowly and gently and the vacuum forms.
- Unfortunately, even with the most careful processing, the contents may start to ferment. During cooling and storage, you should regularly check that the jars are completely sealed and that the vacuum is still present - the lid should bulge inwards. If the lid bulges outwards, the inside has started to ferment and must be discarded.
These were the most popular methods for preserving fruit and vegetables from your own garden. This way you still have some of the delicious summer vegetables in the cold season. If you have any questions or comments, please send us an e-mail at [email protected].
Want to get helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds in the best possible way? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - Your digital bed planner
Annabell
Current Topics in the Community
05 March 2026
@Testi
Show 1 answer@tomatestabtomate
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation
FAQ
You can preserve all kinds of pre-cooked vegetables such as beans or tomatoes or fruit (e.g. cherries, pears or apples) as puree, but sauces are also suitable.
All kinds of fruit are suitable for preserving, such as apples or pears for jam. But you can also preserve vegetables such as beet or beans. Fish, meat, poultry, soups, stews, sauces and pickled vegetables are also suitable.
Fermenting vegetables involves microorganisms such as bacteria and yeasts, which initiate fermentation. This produces lactic acid bacteria, lowers the pH value and inhibits the growth of bacteria and molds. This is how your vegetables are preserved!
How can you preserve vegetables?
There are various ways to preserve fruit and vegetables: Canning or preserving, fermenting vegetables or drying fruit, vegetables, herbs or mushrooms. All of these options will preserve your food for up to a year.